Material Comparison Guide
Research materials to see which options best fit your needs.
Our experienced sales and technical teams are available to assist you with material selection challenges.

What is Material PA66?
Polyamide 66 is a large engineering plastic. This polymer has a density of between 1.12 and 1.14, and is used mainly in the automotive, mechanical, and instrument housing industries. It is a useful material for a variety of applications because of its excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and toughness. However, it has some disadvantages, such as its high water absorption.
Properties
PA66 is a polyamide that has good abrasion resistance, good dimensional stability, and good chemical and impact properties. It is similar to PA6 in structure, and is characterized by zig-zag chain conformation, with intermolecular hydrogen bonds between amide groups. This makes it suitable for use as a reinforcing material and in construction applications. Compared to nylon 6, it has higher tensile strength. Some of its uses include bearings, electrical connections, and structural components. PA66 can also be molded to produce fibers, which are useful in the textile and clothing industries.
PA66 has low viscosity, which allows for molding of thin components. It also has a small shrinkage of 0.1 to 0.02 mm/mm (about 2%). This shrinkage can be reduced by reinforcing it with glass fibers or mineral fillers. It is resistant to most solvents, though it is not resistant to strong acids and chlorinating agents.
Another important feature of polyamide 66 is its high melting point. This feature means that it can be used at higher temperatures, while still maintaining its stiffness. However, it is still hygroscopic, so the degree of hygroscopicity depends on the wall thickness and the composition of the material. It also depends on the environmental conditions. It can be reinforced with various modifiers to enhance its mechanical properties, including synthetic rubber. This can further enhance its impact resistance.
Applications
One of the most popular uses of material PA66 is in cable ties. It is easy to mold and color, and offers a smooth surface pattern. As a result, it has many applications in industrial and consumer products. This versatile material has many advantages over other materials and is a low-cost alternative. For example, it is easier to process than metal and is particularly suitable for products with complex designs. In addition to this, PA66 is stiff and has good creep resistance. These features make it an excellent material for parts used in automobiles.
Another advantage of material PA66 is its low viscosity, allowing it to be molded to a thin component. It can also be reinforced with glass fibers, which reduces shrinkage. It also resists many solvents, although it is not particularly resistant to strong acids or oxidizing agents.
Characteristics
The Physical Characteristics of Material PA66 were studied to determine the proper dose of carbon to be added to PA66 in order to decrease thermal deformation. The latent heat of phase change was measured using an equivalent heat capacity and the specific heat was measured using a differential scanning calorimeter. The remaining physical-performance parameters were determined by the manufacturer.
The dielectric breakdown strength and tensile strength of PA66-GF33% were comparable to the grades of PBT. Nevertheless, the material has a high moisture absorption rate. Lastly, volume resistivity, a measure of insulation properties, was also similar among the two grades. In most resin materials, the volume resistivity is around 1015 O/cm.
In addition, the material’s forming-process parameters were optimized using FDM. The optimal temperature for the nozzle and hot-bed was 240 degC and 90 degC, which minimized warp and displacement during thermal deformation. The moving and extrusion speeds were 30 mm/s and 12.5 mm/s respectively, and the speed to filling ratio was 0.87.
PROPERTIES TABLE OF PA66
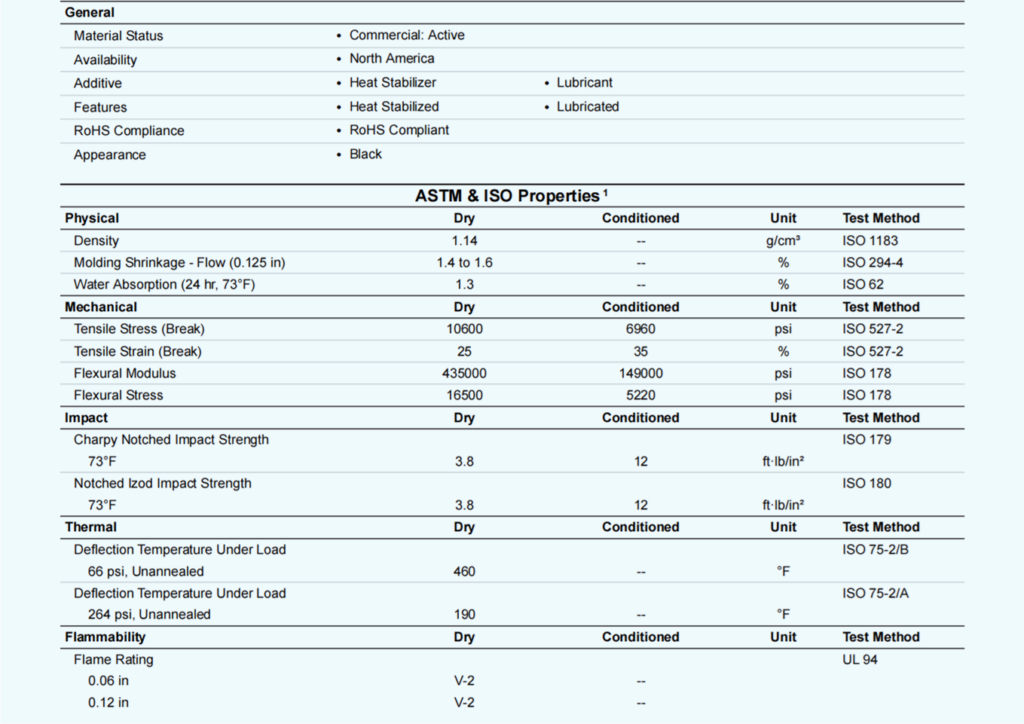
The table data is for reference only, if the plastic type is different and it has different data.

Injection Molding Material Selection
The process of plastic material selection is an integral part of the product design process. By choosing the right material for your application, you can be confident that the product will meet your expectations for quality, cost, and performance. Furthermore, you will save time and money on manufacturing because you will not have to scrap any parts.
We can offer more than 100 different thermoplastic materials. If you are looking for alternative materials, please review our resin substitution guide for ABS, PC, PP,POM,PA,PBT,PPS and other common plastics, or contact us.
Material
- PET
- HDPE
- PC/ABS
- PC/PBT
- PVC
- AS
- PA12
- MDPE
- LDPE
- PEI
- PMMA
- PPE
- EVA
- PC/PMMA
- PA66
- POM
- ABS
- PP
- PBT
- PA6
- PS
- PPO
- PPS
- TPU
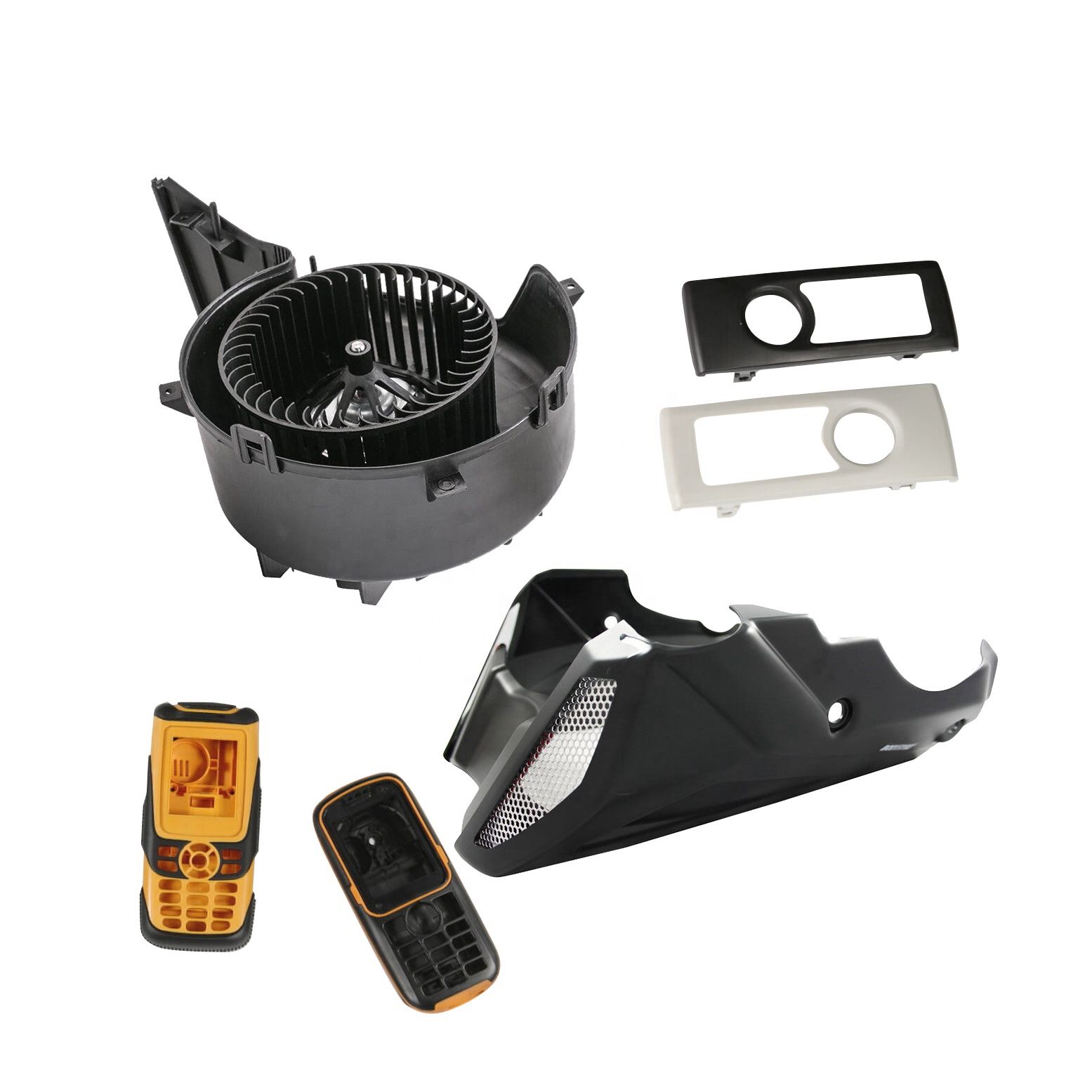
Our PA66 Product Cases

Material: PA66
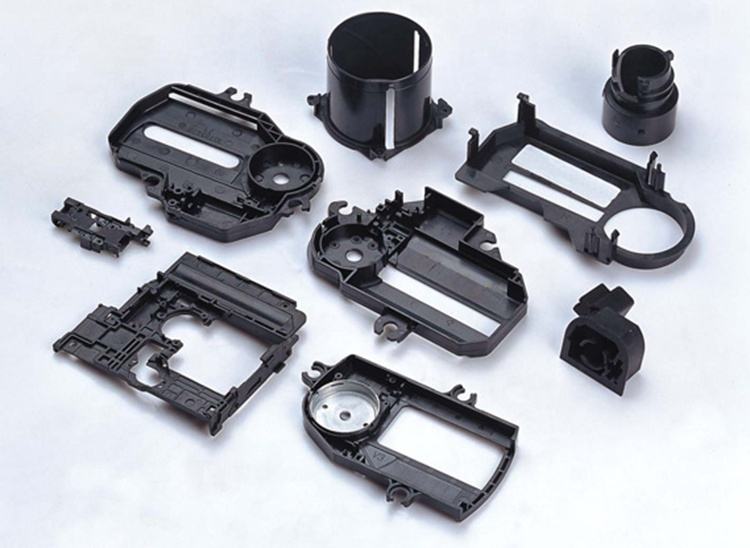

Material:PA66
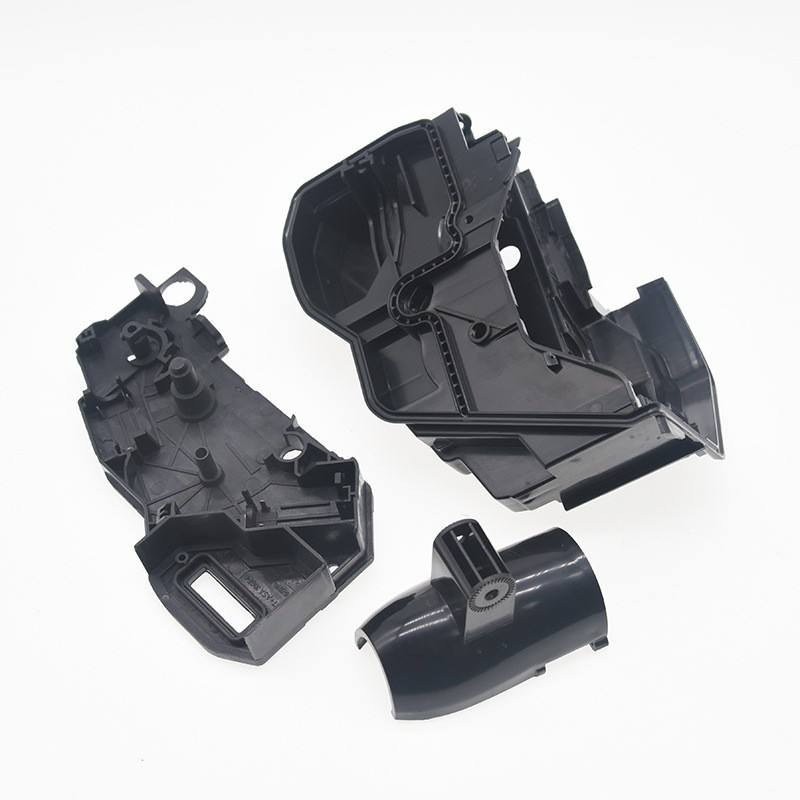

Material: PA66 Black
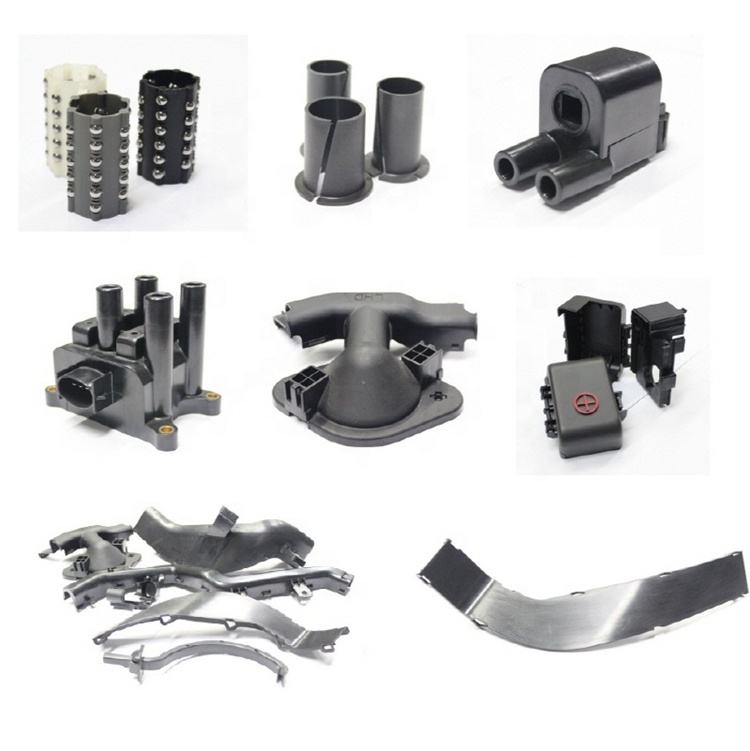

Material:PA66 Insert molding

Material: PA66

How Does Plastic Injection Molding Work?
Plastic injection molding is a process in which plastic pellets are formed and injected into molds to form the desired shape. The plastic melts in a chamber and reaches a specified temperature, so the injection time has to be calculated correctly. Once the desired shape is achieved, the plastic pellets are cooled, and the mold is opened. An ejection bar is then used to force the solid plastic part out of the open cavity.
Additional Links and Resources
Pressure gauges are essential tools used in a wide range of industries to measure and monitor fluid and gas pressure. When it …
Plastic injection molding has become an invaluable tool for businesses and individuals who have a need for custom parts or products. A …
Plastic injection molding is a versatile and reliable process for manufacturing products of all shapes and sizes. It is used in a …
Plastic injection molding is one of the most widely used processes in modern manufacturing. It is used to produce a variety of …





