Injection moulding is a manufacturing process that uses thermoplastic materials to produce objects. Learn about the materials and the process involved in injection moulding. You’ll also learn about the costs associated with the process. Then, you’ll be well-equipped to make the right decisions when looking for a moulding company.
Materials used in injection moulding
Injection moulding is a process where the polymer that is used to form a part is melted in a mould to produce a product. Most polymers are suitable for this process, including thermoplastics, thermosets and elastomers. Since 1995, the number of materials used for this process has increased by about 750 per year. These include both naturally occurring polymers and man-made ones, such as nylon and polyethylene. A variety of alloys have also been developed and are being used for injection moulding. The selection of material depends on the final function, cost and strength of the final product.
Acrylics are common in the automotive industry. These thermoplastics are strong and flexible, yet also lightweight. These properties make them suitable for many applications, including automotive and electronic components. They are also resistant to sunlight and do not absorb odors. This makes them ideal for outdoor use.
Process of injection molding
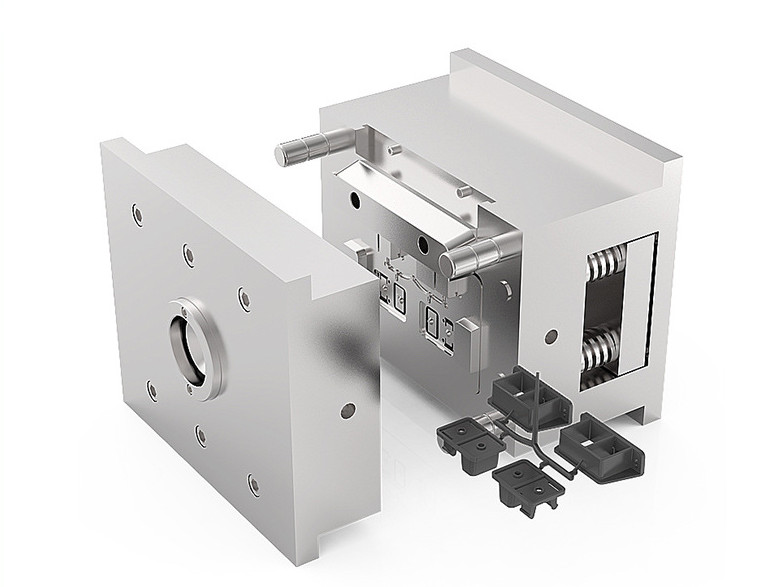
Injection molding is a great way to create complex, intricate parts. This process requires precision in tool design and part design. It can produce highly accurate parts that exhibit excellent dimensional consistency. Automation, robotics, and computer-aided design (CAD) software make it easy to integrate with other manufacturing processes.
The process starts with the filling of plastic pellets into a feed section of the machine. The granules are then compressed and heated through friction. The molten plastic then flows to an injector. This injector can be screw-driven, piston-driven, or manual. The most common type is the hydraulic injector. The molten material is then injected into the cavity of the die and settles within the mold.
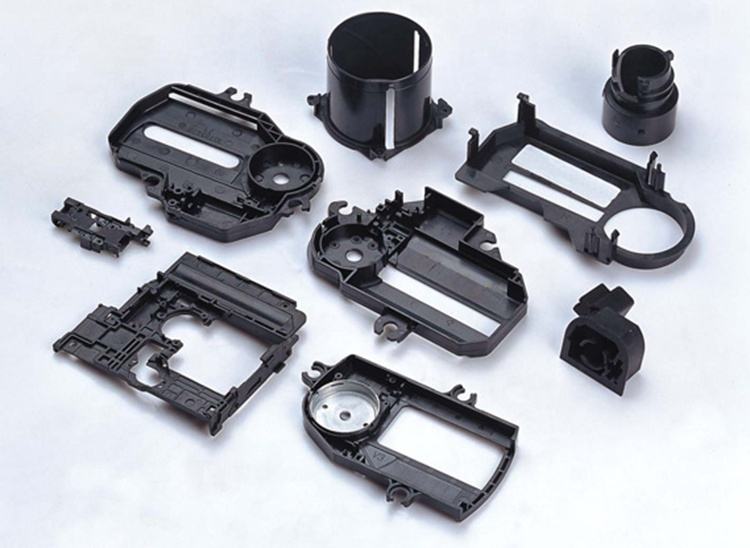
This process is commonly used to manufacture plastic bottles. It is used to create billions of these products each year. It is also used to create electronic housings, including the casings of computers and televisions.

Characteristics of thermoplastics used in injection moulding
Thermoplastics can be used for a variety of applications and offer a variety of properties. These plastics are commonly used in the automotive industry for things like radiator grilles, instrument panels, wheel covers, mirror housings, and consumer electronics. They are also lightweight and flexible.
Thermoplastics can also be used in packaging and construction. Some common thermoplastic materials are HDPE, LLDPE, and PVC. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, LDPE is inexpensive, flexible, transparent, and highly resistant to acids, bases, and vegetable oils. Another popular thermoplastic is HDPE, a sturdy and versatile workhorse polymer that’s used for a wide variety of applications. LLDPE is a softer version of HDPE and is commonly used in consumer products. Polyvinyl chloride, on the other hand, is heavier than most other plastics and is often used for building products.
Nylon is another popular material for injection moulding. Nylon has a wide variety of properties and is one of the cheapest alternatives to rubber. Nylon is also resistant to abrasion and chemicals. It is widely used for injection moulding and other manufacturing processes. Nylon PAs are highly resistant to heat and abrasion, and they offer low coefficients of friction.
Cost of injection moulding
Injection moulding is a popular process for making plastic products. It is an effective method for manufacturing identical parts, and is highly repeatable. It is also relatively cheap, and is an excellent method for producing large series of parts. The cost of injection moulding depends on the complexity of the part and the mould used.
The price of injection moulding depends on the complexity of the part, as well as the number of parameters and design requirements. Most moulds are CNC or EDM machined, or 3D printed. A mould needs to be finished to the required standard, with surface geometries for the part to be molded, runner systems to guide the flow of injected materials, and cooling channels for the mould to cool down properly.